On 27 November 2019, the EU adopted the General Safety Regulation (GSR) , with the aim of drastically reducing the number of deaths, serious injuries and accidents in the EU. This was to be achieved by introducing the latest safety technologies as standard equipment in new vehicles. These systems range from alcohol immobilizers and intelligent speed assistants to tire pressure monitoring systems, lane changing assistants and many other intelligent driver assistance systems. The general requirements apply to passenger cars and light commercial vehicles as well as buses and heavy commercial vehicles. Additional safety requirements have also been imposed on the various types of vehicles. These new requirements will be introduced successively for new car models (EU type-approval) and for vehicle registrations.
The General Safety Regulation – what is it?
Special safety requirements for buses and heavy commercial vehicles
Serious accidents involving heavy commercial vehicles and unprotected persons such as pedestrians and cyclists occur time and time again in urban traffic. This is why the mandatory installation of safety systems for buses and heavy commercial vehicles goes beyond the GSR’s general requirements and existing systems such as lane departure warning systems and emergency brake assistance systems – for example, additional systems are planned that will warn drivers of heavy trucks of pedestrians and cyclists in the blind spot.
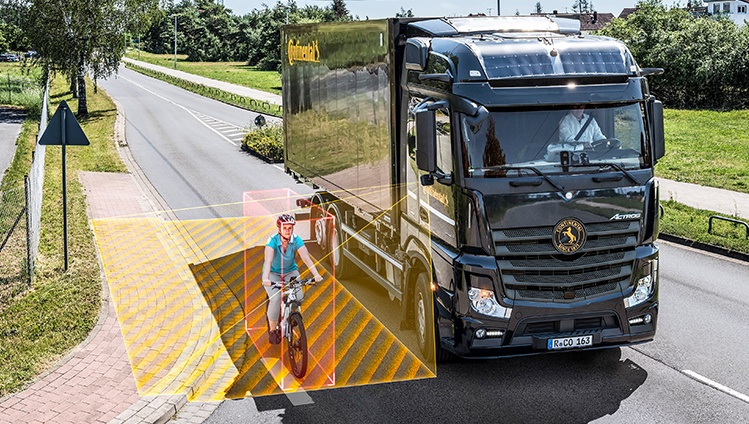
These safety technologies will become mandatory for buses and heavy commercial vehicles:
When will these technologies become mandatory for heavy commercial vehicles and buses?
- From 2022
- From 2024
- From 2026
- From 2029
For EU type-approval:
- Emergency Stop Signal (ESS)
- Alcohol Interlock Installation Facilitation (ALC)
- Driver Drowsiness and Attention Warning (DDR-AW)
- Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)
- Intelligent Speed Assistance (ISA)
- Reversing Detection System (REV)
- Pedestrian and Cyclist Collision Warning (PCW)
- Blind Spot Information System (BLIS)
Modern technologies – an integral part of the implementation of new regulations
In addition to the General Safety Regulation, more packages of measures exist at EU and national levels. With the help of intelligent technologies, these packages are intended to make transport safer, reduce CO2 emissions and ensure fairer competition. With the adoption of Mobility Package I by the European Union in July 2020, the Smart Tachograph, for example, became much more important. It is a control system that documents numerous items of information on driving and rest periods, speed, distance travelled and border crossings, and enables easy controlling procedures by authorities via a standardized interface. Since 2018, e-call is also mandatory in all new models whose EU type-approval is dated after March 31. This automatic emergency call system notifies emergency services in the event of an accident and is expected to save 2,500 lives a year in Europe. The Onboard Weighing System is also a good example of the important role played by modern technologies in new regulations for traffic, transport and vehicle equipment. Based on Directive 96/53/EC regarding the dimensions and weights of heavy commercial vehicles, standardized weighing systems are intended to warn heavy commercial vehicles of overloading, thus avoiding accidents and ensuring fair competition. However, new regulations and related technologies not only lead to safer and cleaner transport, they also increase the overall level of intelligent technologies in vehicles – and this makes them decisive pioneers in autonomous driving.
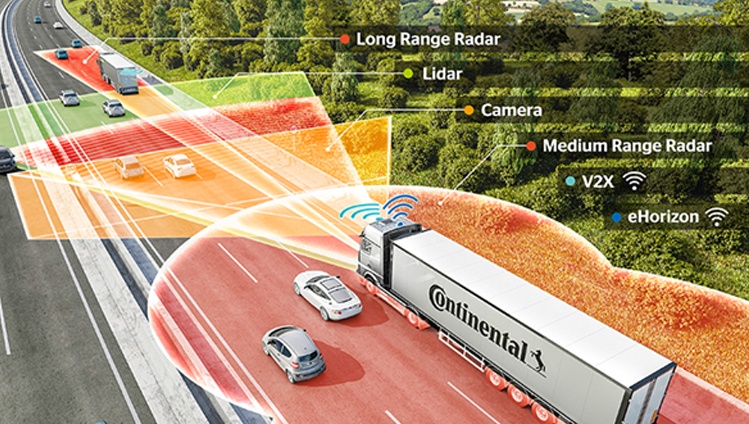

Our solutions for more safety in traffic
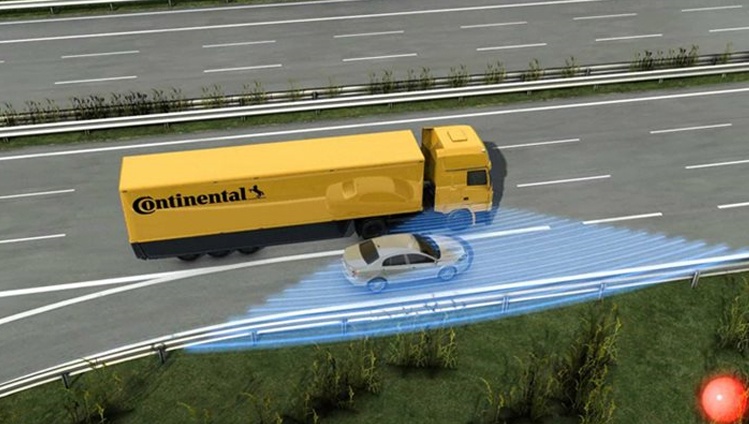
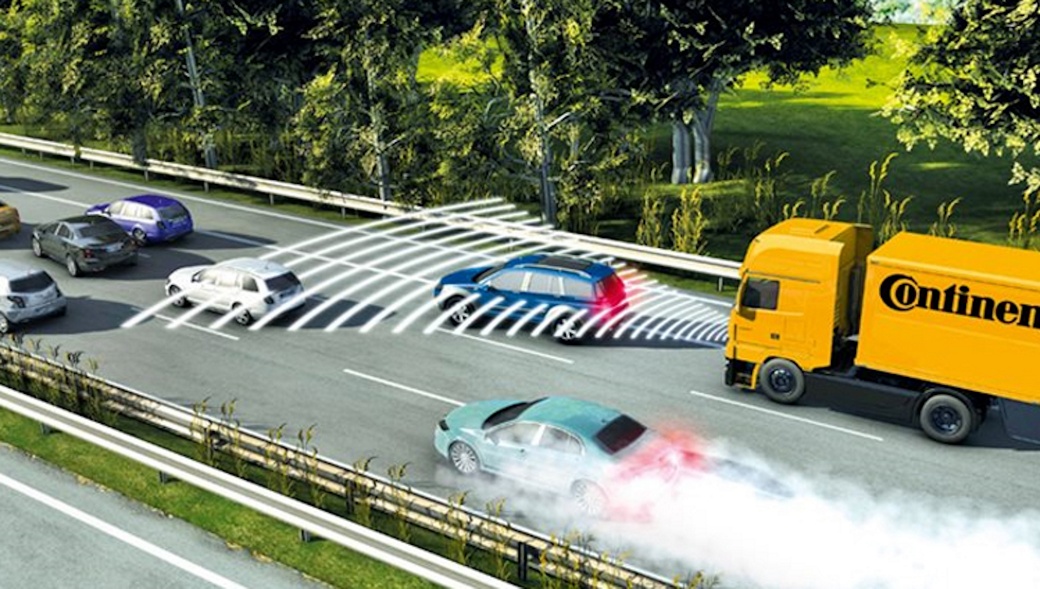
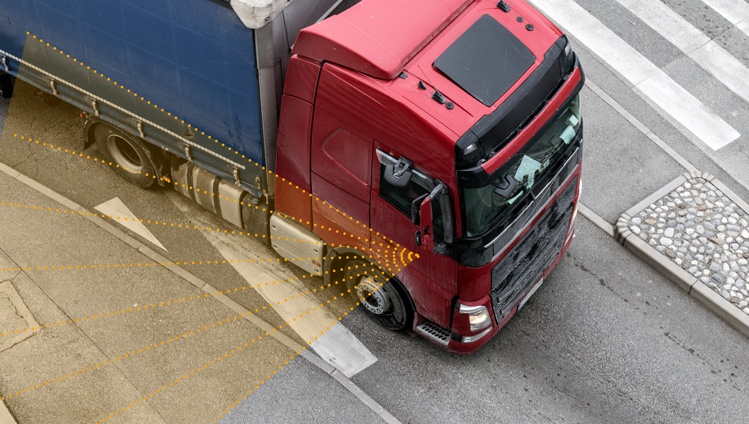


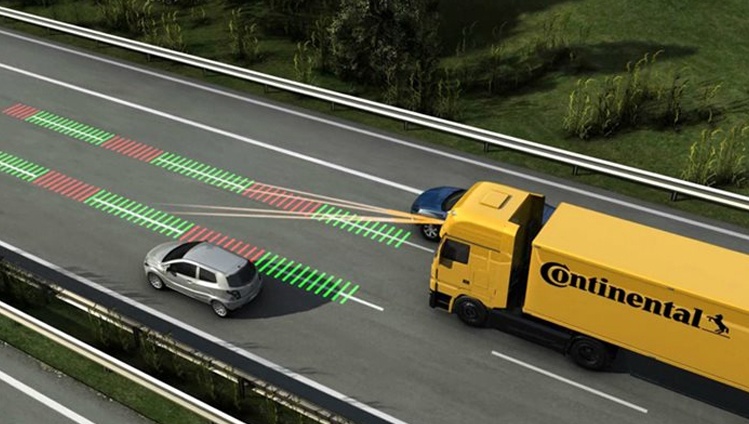



- Blind Spot Detection: Commercial vehicles are large, and their drivers often have limited visibility – despite being generously equipped with mirrors.
- Emergency Brake Assist: Our third-generation radar sensor can trigger a predictive emergency braking system.
- Lane Departure Warning
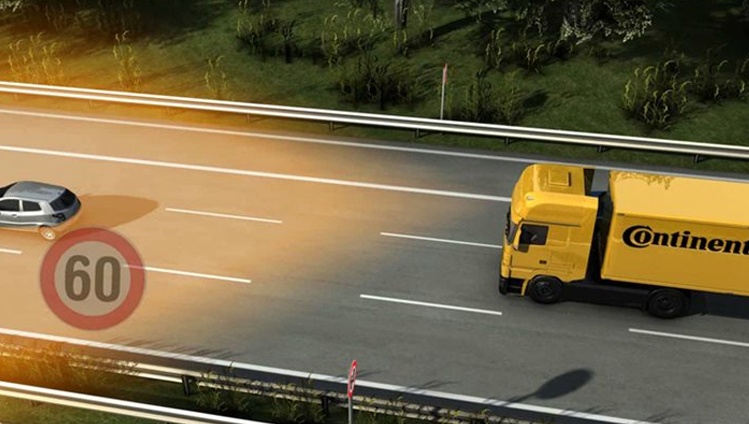
- Traffic Sign Recognition
- Turn Assist RightViu®
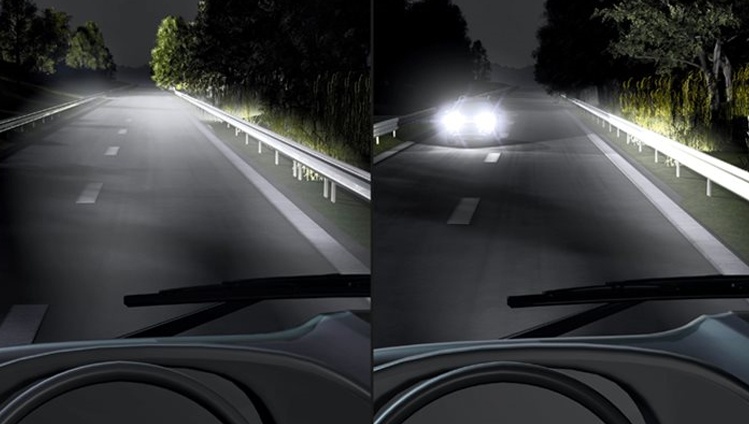
- Intelligent Headlamp Control
Today we are currently developing highly sophisticated driver assistance systems (ADAS) for commercial vehicles to increase safety on the roads. Our radar sensors and camera systems offer a wide range of functions, from emergency brake assistants to turn assist systems and intelligent headlamp assistants. Our objective? To develop reliable safety technologies that go beyond the requirements of the General Safety Regulation.
EU Regulations
Products & Services
Do you want to know more?
*If the contact form does not load, please check the advanced cookie settings and activate the functional cookies for the purpose of contact management.

